Exploring The Wild: Grizzly Or Black Bear – What Sets Them Apart?
When it comes to North America's iconic wildlife, few animals capture the imagination quite like bears. Among them, the grizzly and black bear stand out as majestic yet distinct species. While both are powerful and awe-inspiring creatures, they differ in numerous ways, from their physical traits to their behavior and habitats. Whether you're a wildlife enthusiast, a hiker, or simply someone curious about these magnificent animals, understanding the differences between grizzly and black bears is essential. This knowledge not only helps in appreciating their uniqueness but also ensures safety when encountering them in the wild.
Grizzly bears, often associated with rugged wilderness and untamed landscapes, are known for their immense size and strength. They are a symbol of the wild, thriving in remote areas such as Alaska, Canada, and parts of the northern United States. On the other hand, black bears are more adaptable and widespread, inhabiting forests, swamps, and even suburban areas across North America. Despite their names, black bears can come in a variety of colors, including cinnamon and blonde, which often leads to confusion when distinguishing them from grizzlies.
Both species play vital roles in their ecosystems, contributing to biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance. However, they face challenges such as habitat loss, climate change, and human-wildlife conflicts. By learning more about these bears, we can better appreciate their significance and support conservation efforts aimed at protecting their future. This article dives deep into the world of grizzly and black bears, exploring their characteristics, behaviors, and the steps we can take to coexist peacefully with them.
Read also:Exploring The Life And Legacy Of Clark Mclaughlin Duncan Butler A Remarkable Journey
Table of Contents
- What Makes Grizzly Bears Unique?
- How Do Black Bears Differ from Grizzlies?
- Can You Identify a Grizzly or Black Bear?
- Where Do These Bears Live?
- What Do Grizzly and Black Bears Eat?
- Why Are Bears Important for Ecosystems?
- How Can We Protect Bear Populations?
- What Should You Do If You Encounter a Bear?
What Makes Grizzly Bears Unique?
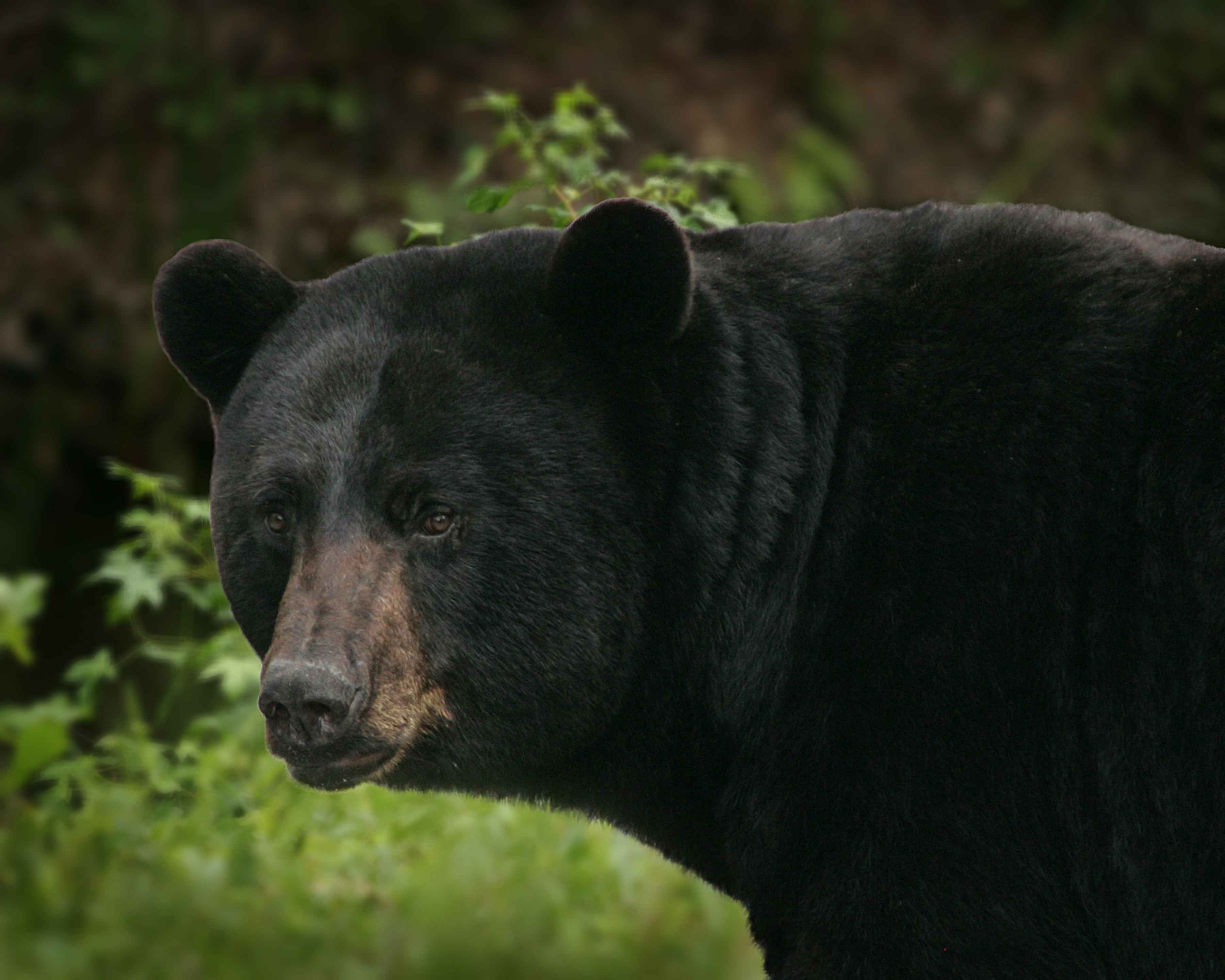
Grizzly bears, scientifically known as Ursus arctos horribilis, are a subspecies of brown bears found primarily in North America. Their name "grizzly" comes from the grizzled or silver-tipped fur that gives them a distinctive appearance. These bears are renowned for their immense size, with males weighing between 400 to 1,200 pounds and standing up to 8 feet tall when on their hind legs. Their muscular build and large shoulder hump, which supports their powerful digging claws, make them easily distinguishable from other bear species.
Grizzlies are solitary animals, often roaming vast territories in search of food. They are omnivores, but their diet is heavily influenced by seasonal availability. In spring, they feed on grasses, roots, and berries, while in summer and fall, they consume more protein-rich foods like salmon, small mammals, and carrion. Their ability to adapt their diet based on the environment is one reason they thrive in diverse habitats, from coastal regions to alpine meadows.
Despite their imposing presence, grizzlies are not aggressive unless provoked. They are more likely to avoid humans than confront them. However, their strength and unpredictability make them formidable animals. Understanding their behavior is crucial for anyone venturing into grizzly country. For instance, grizzlies are known to stand their ground when threatened, and their defensive reactions can be swift and intense. This underscores the importance of respecting their space and adhering to safety guidelines when exploring bear habitats.
What Are the Key Physical Features of Grizzly Bears?
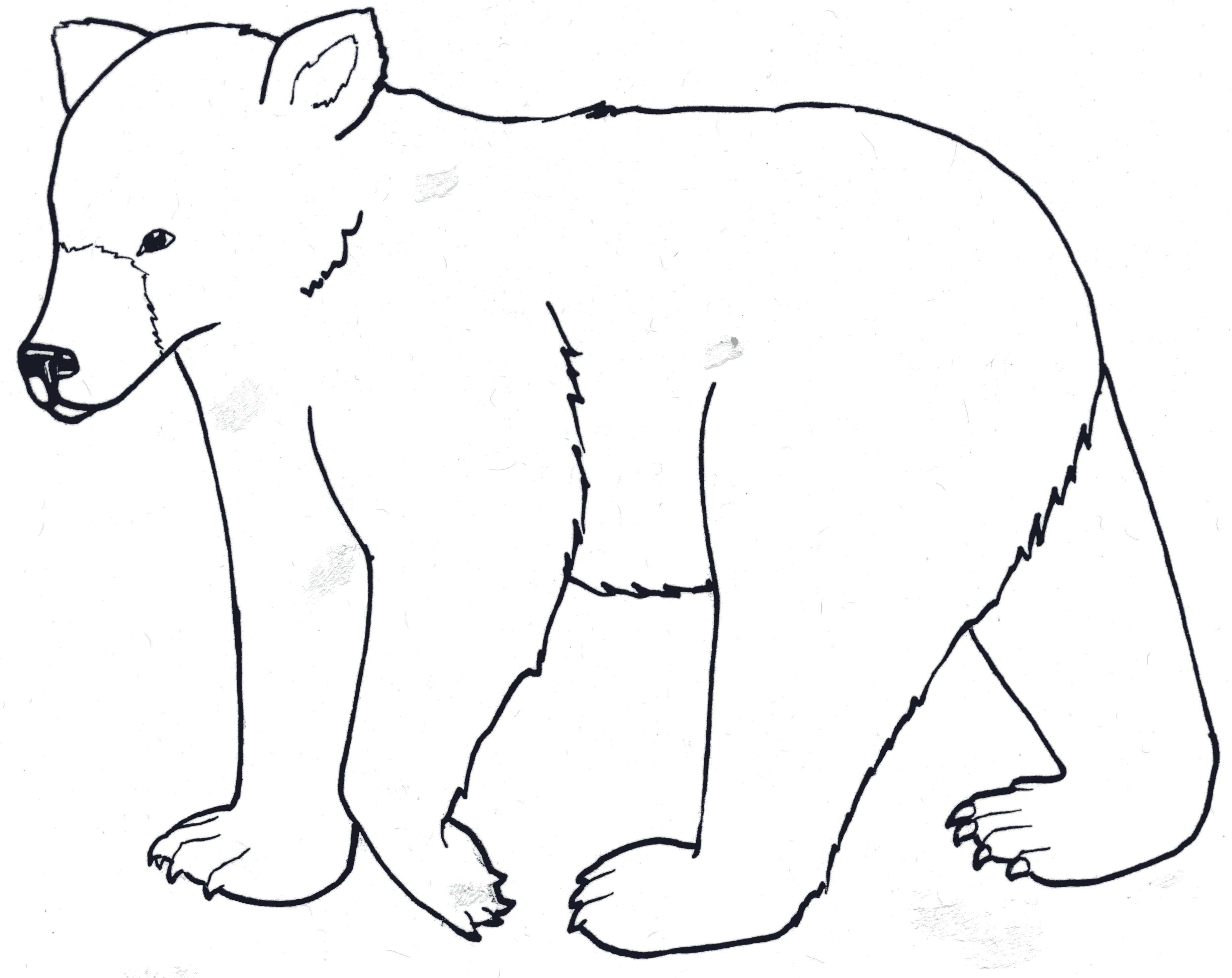
One of the most distinguishing features of grizzly bears is their shoulder hump, which is a mass of muscle that aids in digging and foraging. This hump is absent in black bears, making it a reliable identifier. Additionally, grizzlies have a concave or "dished" facial profile, which contrasts with the straight or slightly convex face of black bears. Their claws are long and curved, typically measuring 2 to 4 inches, and are used for digging roots, excavating dens, and catching prey.
Grizzly bears also have a unique coloration that varies from light brown to nearly black. The silver tips on their fur create a grizzled effect, which is most prominent on their back and shoulders. Their size alone can be intimidating, but it's their combination of physical traits and behavior that truly sets them apart from other bear species.
How Do Grizzlies Communicate?
Grizzly bears use a variety of vocalizations and body language to communicate. Growls, roars, and huffs are common sounds they make when feeling threatened or asserting dominance. They also use scent marking to establish territory and signal their presence to other bears. This behavior is particularly important during mating season, when males compete for access to females. By understanding these communication methods, researchers can gain insights into their social dynamics and behavior in the wild.
Read also:Does Barron Trump Really Sing Uncovering The Truth And More
How Do Black Bears Differ from Grizzlies?
Black bears, scientifically known as Ursus americanus, are the smallest of the three bear species found in North America. Despite their name, their fur can range from jet black to cinnamon, blonde, or even white, as seen in the rare Kermode or "spirit bear." On average, adult male black bears weigh between 200 to 600 pounds, making them significantly smaller than grizzlies. Their build is more streamlined, and they lack the prominent shoulder hump that characterizes grizzly bears.
Unlike grizzlies, black bears are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, from dense forests to suburban areas. Their diet is primarily plant-based, consisting of fruits, nuts, and vegetation, but they are opportunistic feeders and will consume insects, fish, and small mammals when available. This adaptability has allowed black bears to maintain stable populations across much of North America, even in areas where grizzlies have disappeared.
Black bears are generally more timid and less confrontational than grizzlies. They are more likely to flee when encountering humans, although they can become aggressive if they feel cornered or if their cubs are threatened. Understanding their behavior and habitat preferences is essential for minimizing conflicts and ensuring their conservation.
What Are the Behavioral Differences Between Black Bears and Grizzlies?
One of the most notable differences between black bears and grizzlies is their response to threats. Grizzlies are more likely to stand their ground and defend themselves, while black bears typically retreat or climb trees to escape danger. This behavioral distinction is crucial for hikers and campers, as it influences how they should react during an encounter. For example, playing dead is recommended if attacked by a grizzly, whereas fighting back is advised if confronted by a black bear.
Another key difference lies in their foraging habits. Black bears are excellent climbers and often use trees to access food, such as nuts or honey from beehives. Grizzlies, on the other hand, rely on their strength and digging ability to uncover food sources. These differences in behavior and diet reflect their distinct evolutionary adaptations to their respective environments.
How Do Black Bears Adapt to Urban Environments?
Black bears have shown remarkable adaptability to human-altered landscapes. In some regions, they have learned to associate humans with food, leading to increased encounters in suburban areas. While this adaptability has helped them survive, it also poses challenges, such as vehicle collisions and conflicts with property owners. Conservation efforts focus on educating the public about bear-proofing garbage cans and reducing attractants to minimize these risks.
Can You Identify a Grizzly or Black Bear?
Identifying a grizzly or black bear in the wild requires careful observation of physical and behavioral traits. While size and color can provide clues, they are not always reliable indicators. For instance, a large black bear may appear similar to a small grizzly, and color variations can make identification challenging. Instead, focus on key distinguishing features such as the shoulder hump, facial profile, and claw length.
Grizzly bears have a pronounced shoulder hump, a concave facial profile, and long, curved claws. Their ears are rounded and relatively small compared to their head size. Black bears, in contrast, lack a shoulder hump, have a straight or convex facial profile, and shorter, more curved claws. Their ears are taller and more pointed, giving them a distinct appearance.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Bear Identification?
One common misconception is that black bears are always black, and grizzlies are always brown. In reality, both species exhibit a wide range of color variations. Another misconception is that size alone can determine the species. While grizzlies are generally larger, there is significant overlap in size between the two species. Relying on these misconceptions can lead to incorrect identification, which is why understanding their physical and behavioral traits is essential.
How Can You Use Tracks to Identify Bear Species?
Bear tracks can provide valuable clues for identification. Grizzly tracks are larger and show long claw marks extending beyond the toes, while black bear tracks have shorter claws and a more rounded appearance. The shape of the footpad and the spacing between toes can also help distinguish between the two species. Learning to recognize these differences is a useful skill for wildlife enthusiasts and outdoor adventurers.
Where Do These Bears Live?
Grizzly and black bears inhabit different regions based on their ecological requirements. Grizzlies are primarily found in remote wilderness areas, such as Alaska, western Canada, and parts of the northwestern United States, including Montana, Wyoming, and Idaho. They prefer open landscapes with abundant food sources, such as river valleys and mountain meadows.
Black bears, on the other hand, are more widespread and adaptable. They inhabit forests, swamps, and even suburban areas across Canada, the United States, and northern Mexico. Their ability to thrive in diverse environments has allowed them to maintain larger populations compared to grizzlies. However, habitat fragmentation and human encroachment continue to pose challenges for both species.
What Are the Conservation Challenges Facing Bear Habitats?
Habitat loss due to logging, agriculture, and urban development is a major threat to bear populations. Climate change also impacts their food sources, particularly for grizzlies that rely on salmon and other seasonal resources. Conservation efforts focus on protecting critical habitats, creating wildlife corridors, and promoting coexistence between humans and bears.
How Do Bears Adapt to Seasonal Changes in Their Environment?
Bears are highly attuned to seasonal changes and adjust their behavior accordingly. In autumn, they enter a phase of hyperphagia, consuming vast amounts of food to build fat reserves for hibernation. During winter, they retreat to dens and enter a state of dormancy, surviving on stored fat. This adaptation allows them to endure harsh conditions and emerge in spring ready to resume their activities.
What Do Grizzly and Black Bears Eat?
Grizzly and black bears are omnivores, but their diets differ based on their habitats and available resources. Grizzlies have a more varied diet, including plants, fish, and mammals, while black bears rely heavily on vegetation and insects. Understanding their dietary preferences provides insights into their ecological roles and conservation needs.
How Do Bears Forage for Food?
Bears use their keen sense of smell and strong limbs to locate and access food. Grizzlies dig for roots and excavate burrows, while black bears climb trees to reach fruits and nuts. Their foraging behavior influences their movements and interactions with other wildlife.
What Role Do Salmon Play in Grizzly Bear Diets?
For coastal grizzlies, salmon are a critical food source during spawning season. Bears congregate at rivers and streams to catch fish, which provide essential fats and proteins. This behavior highlights the interconnectedness of ecosystems and the importance of protecting salmon populations.
Why Are Bears Important for Ecosystems?
Bears play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. As apex predators and seed dispersers, they influence the distribution of plants and animals. Their presence benefits biodiversity and supports healthy ecosystems.
How Do Bears Contribute to Seed Dispersal?
Bears consume fruits and berries, spreading seeds through their droppings. This process aids in plant regeneration and forest growth, demonstrating their ecological significance.
What Happens When Bear Populations Decline?
Decl