Exploring The Majestic Rivers In Kenya Africa: A Natural Wonder
These rivers carve through the country’s varied terrains, providing essential resources like water, fertile soil, and habitats for countless species. They are also deeply intertwined with Kenya’s history, culture, and traditions, making them more than just geographical features—they are symbols of life and resilience. As we delve deeper into the story of rivers in Kenya Africa, it becomes evident how they shape the lives of millions. Farmers rely on their waters for irrigation, fishermen depend on them for livelihoods, and wildlife thrives in the lush ecosystems they nurture. Beyond their practical importance, these rivers are also central to Kenya's tourism industry, offering opportunities for adventure, exploration, and relaxation. Whether it’s a thrilling rafting expedition or a peaceful birdwatching session, the rivers of Kenya are a magnet for both local and international visitors. This article will take you on a journey through the most significant rivers in Kenya Africa, uncovering their ecological, cultural, and economic significance. We’ll explore their origins, courses, and the challenges they face in the modern world. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of why these rivers are not just natural wonders but also vital lifelines for Kenya and its people.
Table of Contents
- Why Are Rivers in Kenya Africa So Important?
- What Are the Major Rivers in Kenya Africa?
- How Do Rivers in Kenya Africa Support Biodiversity?
- How Are Rivers in Kenya Africa Used for Agriculture?
- What Are the Challenges Facing Rivers in Kenya Africa?
- How Can We Protect Rivers in Kenya Africa for Future Generations?
- What Role Do Rivers Play in Kenya's Tourism Industry?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Rivers in Kenya Africa
Why Are Rivers in Kenya Africa So Important?
Rivers in Kenya Africa are the backbone of the nation’s ecosystems and economy. They provide essential resources such as water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use, making them indispensable for daily life. These rivers also serve as natural highways, connecting remote areas to urban centers and facilitating trade and transportation. Beyond their practical uses, rivers are deeply embedded in Kenya’s cultural fabric, featuring prominently in local folklore, rituals, and traditions.
Ecologically, rivers in Kenya Africa are biodiversity hotspots. They support a wide variety of flora and fauna, including rare and endangered species. For instance, the Tana River is home to the Tana River mangabey, a critically endangered primate found nowhere else in the world. Similarly, the Mara River is a lifeline for the iconic wildebeest migration in the Maasai Mara, one of Africa’s greatest natural spectacles. These rivers also help regulate the climate by maintaining humidity levels and supporting vegetation that absorbs carbon dioxide.
Read also:Is Trump Lefthanded Unveiling The Truth About Donald Trumps Handedness
Why Are Rivers Essential for Kenya’s Communities?
Communities across Kenya depend on rivers for survival. In rural areas, rivers provide water for domestic use and livestock, while in urban centers, they are crucial for sanitation and industrial processes. The rivers also play a significant role in energy production, with several hydroelectric dams harnessing their power to generate electricity. For example, the Seven Forks Dam on the Tana River supplies a substantial portion of Kenya’s energy needs.
What Are the Economic Benefits of Rivers in Kenya Africa?
The economic importance of rivers in Kenya Africa cannot be overstated. They support agriculture, which is the backbone of the country’s economy, by providing water for irrigation. Rivers also attract tourists, who come to enjoy activities like rafting, fishing, and wildlife safaris. This influx of visitors generates revenue and creates jobs, contributing to Kenya’s GDP. Additionally, rivers support fisheries, providing a source of protein and income for many families.
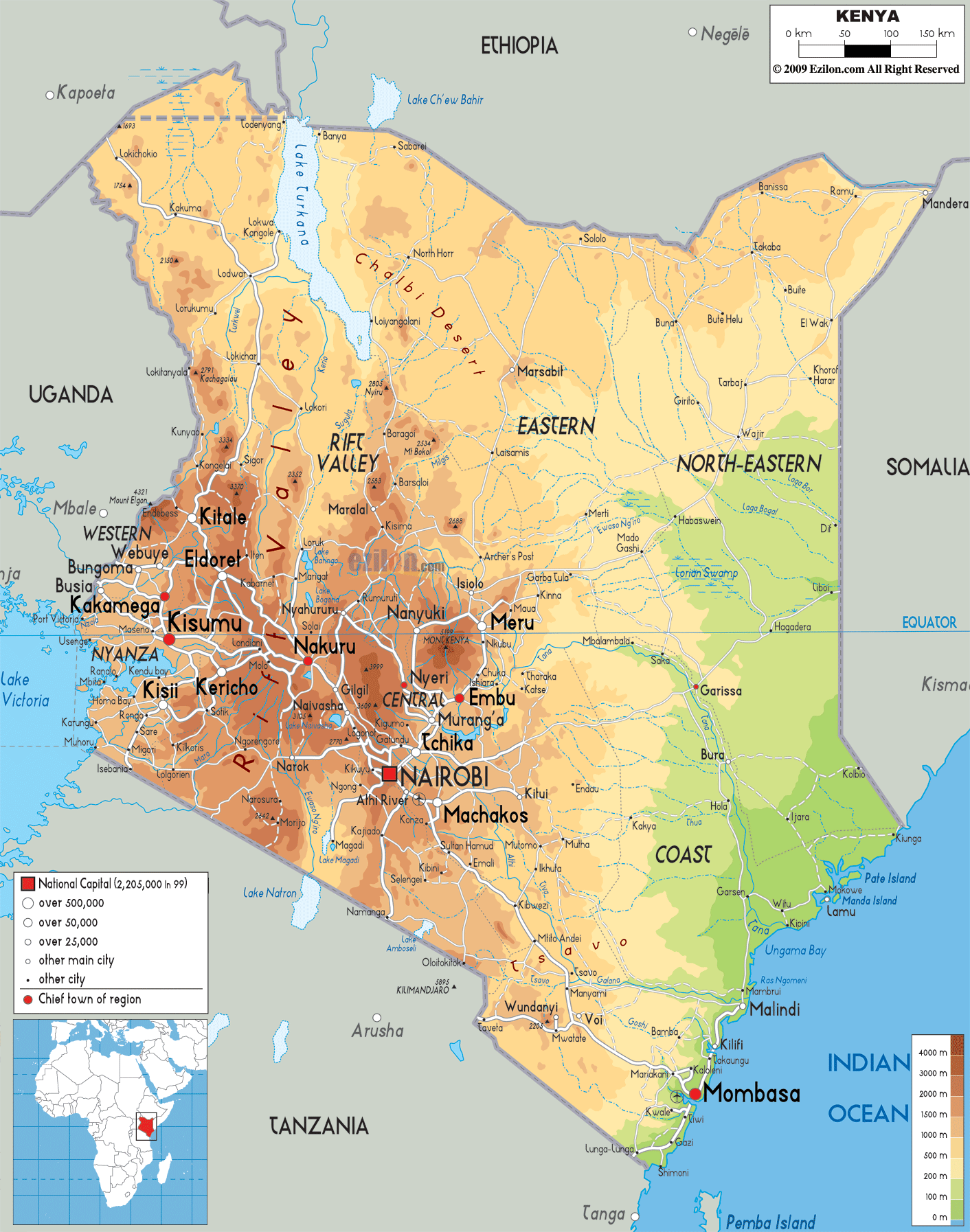
What Are the Major Rivers in Kenya Africa?
Kenya boasts several major rivers, each with its unique characteristics and significance. Among them, the Tana River stands out as the longest river in Kenya, stretching over 700 kilometers. Originating in the Aberdare Mountains and flowing into the Indian Ocean, the Tana River supports diverse ecosystems and is a vital resource for agriculture and energy production.
Another prominent river is the Athi-Galana-Sabaki, which flows through Nairobi and Mombasa before emptying into the Indian Ocean. This river is crucial for urban water supply and supports the livelihoods of communities along its banks. The Mara River, though shorter, is globally renowned for its role in the annual wildebeest migration, making it a cornerstone of Kenya’s tourism industry.
What Makes the Tana River Unique?
The Tana River is not only Kenya’s longest river but also one of its most ecologically diverse. It flows through a variety of landscapes, including forests, savannas, and wetlands, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species. The river’s delta is a Ramsar site, recognized for its international importance as a wetland habitat. Additionally, the Tana River Basin is a critical agricultural zone, producing crops like rice, sugarcane, and maize.
How Does the Mara River Impact Wildlife Migration?
The Mara River is synonymous with the Great Migration, an annual event where millions of wildebeest, zebras, and other herbivores traverse the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem in search of greener pastures. The river serves as a natural barrier, creating dramatic crossings that are a highlight for tourists. These crossings are also a testament to the river’s ecological importance, as they help maintain the balance of predator and prey populations in the region.
Read also:Discover The Ultimate Guide To S 4u Hub A Comprehensive Resource
How Do Rivers in Kenya Africa Support Biodiversity?
Rivers in Kenya Africa are teeming with life, providing habitats for countless species of plants, fish, birds, and mammals. These waterways act as corridors, connecting different ecosystems and allowing species to migrate and disperse. For example, the Tana River Basin hosts over 200 bird species, many of which are migratory, making it a paradise for birdwatchers.
Additionally, rivers create microclimates that support unique vegetation. The riparian forests along riverbanks are home to rare and endemic species, such as the Tana River red colobus monkey. These forests also play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion and maintaining water quality, ensuring the river ecosystems remain healthy and vibrant.
How Do Rivers Influence Kenya’s Ecosystems?
Rivers in Kenya Africa are the lifeblood of the country’s ecosystems, sustaining both terrestrial and aquatic life. They provide breeding grounds for fish and amphibians, while their floodplains support herbivores like elephants and buffaloes. The seasonal flooding of rivers enriches the soil, promoting the growth of lush vegetation that attracts herbivores and, in turn, predators.
How Are Rivers in Kenya Africa Used for Agriculture?
Agriculture is the backbone of Kenya’s economy, and rivers play a pivotal role in this sector. Farmers rely on rivers for irrigation, especially in arid and semi-arid regions where rainfall is unpredictable. The Tana River, for instance, supports large-scale irrigation projects that produce crops like rice, maize, and sugarcane.
Small-scale farmers also benefit from rivers, using traditional methods to water their crops and sustain their livestock. In addition to irrigation, rivers provide fertile alluvial soils that are ideal for farming. This agricultural productivity not only feeds the nation but also contributes to Kenya’s exports, enhancing its economic stability.
What Are the Challenges of River-Based Agriculture?
While rivers in Kenya Africa are a boon for agriculture, they also present challenges. Over-extraction of water for irrigation can lead to reduced river flows, affecting downstream ecosystems and communities. Pollution from agricultural runoff, including pesticides and fertilizers, poses another threat, degrading water quality and harming aquatic life.
What Are the Challenges Facing Rivers in Kenya Africa?
Despite their importance, rivers in Kenya Africa face numerous threats, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. Deforestation along riverbanks leads to soil erosion, which increases sedimentation and reduces water quality. Industrial and domestic waste further exacerbates pollution, endangering aquatic life and human health.
Climate change poses an additional challenge, with erratic rainfall patterns and prolonged droughts affecting river flows. This not only impacts biodiversity but also threatens the livelihoods of communities that depend on rivers for water and food. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts from governments, NGOs, and local communities.
How Can We Address Pollution in Kenya’s Rivers?
Pollution is one of the most pressing issues facing rivers in Kenya Africa. To combat this, stricter regulations on industrial waste disposal and better wastewater treatment systems are needed. Public awareness campaigns can also encourage communities to adopt sustainable practices, such as proper waste management and reduced use of harmful chemicals.
How Can We Protect Rivers in Kenya Africa for Future Generations?
Protecting rivers in Kenya Africa requires a multi-faceted approach that combines conservation, education, and policy reforms. Reforestation efforts along riverbanks can help prevent soil erosion and restore degraded ecosystems. Community-based initiatives, such as river clean-up drives and sustainable fishing practices, can also make a significant impact.
Education plays a crucial role in fostering a culture of conservation. By teaching children and adults about the importance of rivers, we can inspire them to take action. Finally, governments must implement and enforce policies that safeguard river ecosystems, ensuring they remain vibrant and productive for future generations.
What Role Can Technology Play in River Conservation?
Technology offers innovative solutions for protecting rivers in Kenya Africa. Remote sensing and satellite imagery can monitor river health and detect changes in water quality or flow. Mobile apps can engage citizens in reporting pollution incidents, while advanced filtration systems can treat wastewater more effectively.
What Role Do Rivers Play in Kenya's Tourism Industry?
Rivers in Kenya Africa are a cornerstone of the country’s tourism industry, attracting visitors from around the globe. Activities like white-water rafting on the Tana River, fishing in Lake Victoria’s tributaries, and wildlife safaris along the Mara River offer unforgettable experiences. These rivers also provide stunning backdrops for lodges and campsites, enhancing the appeal of Kenya’s natural landscapes.
How Do Rivers Contribute to Adventure Tourism?
Adventure tourism is a growing sector in Kenya, and rivers play a central role in this trend. The rapids of the Tana River and the Athi-Galana-Sabaki offer thrilling opportunities for rafting and kayaking. Meanwhile, the serene waters of smaller rivers provide ideal conditions for canoeing and paddleboarding, catering to a wide range of interests.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rivers in Kenya Africa
What Is the Longest River in Kenya?
The Tana River is the longest river in Kenya, stretching over 700 kilometers from its source in the Aberdare Mountains to its mouth at the Indian Ocean.
How Do Rivers in Kenya Africa Support Wildlife?
Rivers provide water, food, and breeding grounds for wildlife, sustaining diverse ecosystems. They also facilitate the movement of animals during migrations, such as the Great Migration in the Maasai Mara.
What Are the Main Threats to Rivers in Kenya Africa?
The main threats include deforestation, pollution, over-extraction of water, and climate change. These challenges impact both the ecological health of rivers and the communities that depend on them.
In conclusion, rivers in Kenya Africa are not just geographical features but vital lifelines that sustain ecosystems, communities, and economies. By understanding their significance and addressing the challenges they face, we can ensure these majestic waterways continue to thrive for generations to come. For more information on Kenya’s natural wonders, visit Kenya Wildlife